Reciprocating compressors have a lot of moving parts, and because of this, regular maintenance is important. This ensures that all the compressor components are able to function at their peak efficiency while also preventing wear that will lead to a shortened lifespan and additional maintenance costs.
Therefore, this article will provide you with a guide on the sort of things you should be regularly checking on your reciprocating air compressor.
Table of Contents
- Reciprocating Air Compressor Maintenance Tips
- Reciprocating Air Compressor Maintenance Checklist Example
- The Importance of Proper Preventative Maintenance Checks
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Reciprocating Air Compressor Maintenance Tips
To keep your reciprocating air compressor at optimum performance, you will have to keep on top of it and take some measures. The air compressor itself will not be able to maintain itself, hence, you will need to carry out maintenance to help prolong the reciprocating compressor’s lifespan.
Some of the measures you can take include:
- Minimizing vibrations
- Monitoring temperatures
- Conducting oil maintenance
- Keeping the air compressor clean
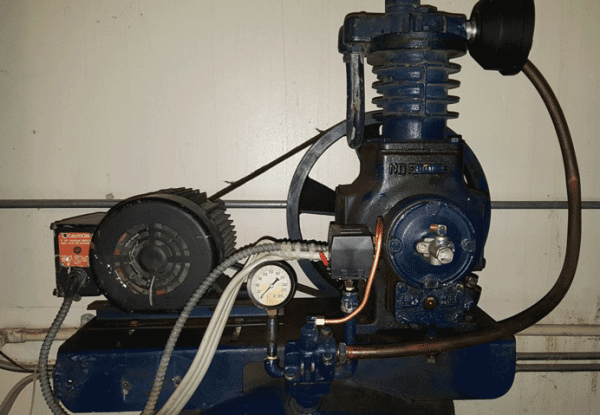
Minimizing Vibrations
Vibration is a very common issue that can lead to reciprocating compressor failure. Why will vibrations occur? It’s likely that some of the reciprocating compressor parts are not properly secured. Constant vibrations will lead to additional parts becoming loose, leading to misalignment, excessive wear, and further mechanical problems.
You must ensure that the air compressor is tightly secured on a flat surface, and use vibration pads if necessary to help with minimizing/eliminating any vibrational issues.
Monitoring Temperatures
It’s likely that you will witness a sudden spike in the reciprocating compressor’s temperature during operation at some point, if this occurs you should shut down the compressor immediately. If a reciprocating compressor is allowed to run at high temperatures for extended periods then it is undoubtedly going to lead to premature component failure.
Usually, the compressors will be equipped with a thermal overload switch, which essentially protects the motor from overheating to prolong its life. The reciprocating compressor may not have one, or if the switch becomes faulty, you will have issues; so it is always worth keeping an eye on the temperature.
It’s important to apply proper bearing greasing per the operator’s manual and keep the motor clean from debris and dirt, this will help ensure you are prolonging your compressor’s use. Another reason for potential temperature spikes is the oil level dropping too low, which leads us on to the next point!
Conducting Oil Maintenance
When to add or change reciprocating air compressor oil will depend on many factors, such as the reciprocating compressor model and the environmental conditions. Manufacturers, in general, will recommend that the oil be changed on a quarterly basis.
This may not always be the case, however, as if you use your compressor more frequently then you may need to change the oil sooner. Some oil producers will design lubricants that are made for extended periods of use and will recommend that you change the oil after say a year or 2000 hours of use, whichever comes first.
The operator should also regularly monitor the oil level as part of their regular checks. You might be lucky and have a reciprocating compressor that is equipped with a low oil level monitoring system, helping you prevent damage or pump failure when a compressor runs on too little oil. For more information on compressor oil and changing it, visit our How to Change Air Compressor Oil – Guide to Replacing Compressor Oil!
Keeping the Air Compressor Clean
A major cause of premature reciprocating air compressor equipment failure is excess dirt and debris within the system. The operator will play an important role in the preventive maintenance process by watching out for any accumulation of dirt and removing at quickly as possible.
It can be as simple as cleaning or blowing off any contaminants with compressed air on a regular basis to ensure that your air compressor components are kept clean, along with changing the air filter regularly and when necessary. For more information on an air intake filter, visit our Air Compressor Air Intake Filter – Replacing, Locating, Cleaning & Purpose Guide!
Reciprocating Air Compressor Maintenance Checklist Example
I have picked out this example of maintenance guidelines, or a checklist, provided by Ingersoll Rand in their oil-less reciprocating air compressor manual!
First, it states that you should switch the main disconnect switch to the “off” position to ensure no power is entering the unit before performing any maintenance function. “Lock out” or “tag out” all sources of power and be sure that all air pressure in the unit is relieved. Failure to do this may result in injury or equipment damage – a warning not to be meddled with.
It’s important to note that this is simply an example of a reciprocating compressor checklist, and your compressed air systems may not have all the same components and follow the same list. Hence, it is recommended that you only use this as guidance, and refer to your reciprocating compressor owner’s manual or contact your manufacturer for specific guidelines.
Daily Maintenance
- Drain moisture from the reciprocating compressor tank by operating the tank drain located at the bottom of the tank. Do not open the drain valve if the tank pressure exceeds 25 PSIG. Visit our guide on How Often To Drain Air Compressor Tank to learn more!
- Turn off the reciprocating compressor at the end of each day’s operation. Turn off power supply at wall switch.
Weekly Maintenance
- Clean dust and other particulates from the cylinder, cylinder head, motor, fan blade, air lines, and tank.
- Remove and clean air intake filters.
- Check V-belts for tightness. The V-belts must be tight enough to transmit the necessary power to the compressor. Adjust the V-belts as follows:
Remove bolts and guard to access the compressor drive.
Loosen mounting hardware, which secures motor to base. Slide motor within slots of baseplate to desired position.
Apply pressure with finger to one belt at midpoint span. Tension is correct if top of belt aligns with bottom of adjacent belt. Make further adjustments if necessary.
Check the alignment of pulleys. Adjust if necessary.
Tighten mounting hardware to secure motor on base.
Re-install guard and secure bolts.
Note: Do not exceed 15 PSIG nozzle pressure when cleaning element parts with compressed air. Do not direct compressed air against human skin. Serious injury could result. Never wash elements in fuel oil, gasoline, or flammable solvent.
Every 90 Days or 500 Hours Maintenance
- Check entire system for air leakage around fittings, connections, and gaskets, using soap solution and brush.
- Tighten nuts and cap screw as required.
- Check and clean air compressor system valves as required. Replace when worn or damaged parts.
General Maintenance Notes
Pressure Relief Valve
The pressure relief valves are automatic pop valves. Each valve is adjusted for the maximum pressure of the unit on which it is installed. If it should pop, it will be necessary to drain all the air out of the tank in order to reseat properly or drop the pressure in the line. Do not readjust the pressure relief valves.
Tank Drain Valve
The drain valve is located at the bottom of the tank. Open the drain valve daily to drain condensation. Do not open the drain valve if tank pressure exceeds 25 psi. The automatic tank drain equipped reciprocating compressor requires draining manually once a week.
Pressure Switch
The pressure switch is automatic and will start the reciprocating air compressor at the low pressure and stop at the maximum pressure when it is reached. The pressure switch diaphragm is adjusted to start and stop the reciprocating air compressor at the proper pressure for the unit on which it is installed. Do not readjust.
Reciprocating Compressor Cylinder Valves
Once per year or if the reciprocating compressor fails to pump air or seems slow in filling up the tank, disconnect the unit from the power source, remove the valve plate, and clean thoroughly, using compressed air. The valve plates can be reached by removing the cylinder head. The cylinder head is held by four capscrews. Take care not to damage the O-ring seal under the top of the cover.
After cleaning with exceptional care, make sure that all parts are replaced in exactly the same position and that all joints must be tight or the compressor will not function properly. When all valves are replaced and connections tight, close the hand valve at the tank outlet for the final test.
All valves must be replaced in their original position. Valve gaskets should be replaced each time valves are serviced.
Check Valve
The tank check valve closes when the compressor stops operating, preventing air from flowing out of the tank through the unloader valve. After the compressor stops operating, if air continues to escape through the unloader solenoid valve, it is an indication that the check valve is leaking.
This can be corrected by removing the check valve and cleaning the disc and seat. If the check valve disc is worn badly, replace same.
Belts
Drive belts must be kept tight enough to prevent slipping. If belts slip or squeak, see V-belt maintenance.
Motor Lubrication
Long time satisfactory operation of an electric motor depends in large measure on proper lubrication of the bearings. Bearing grease will lose its lubricating ability over time, not suddenly. Refer to the motor manufacturer’s instructions for the type of grease and lubrication intervals.
Pilot Valve
The pilot valve actuates the head unloader mechanism to provide a means of stopping or starting the compression of air by the compressor without stopping or starting the electric motor.
Alternative Measures
As this was an oil-less reciprocating air compressor manual, it evidently missed out on a few steps that oil-lubricated reciprocating air compressors would include. Therefore, here is a list of some additional measures you could take:
- Maintain lubricant level as recommended by the manufacturer. Check the lubricant level several minutes after the compressor has run. (Daily)
- Check for oil leaks. (Daily)
- Inspect lubricant for contamination and change if necessary. (Weekly)
- Change oil. (Annually)
The checklist mentioned checking for air leaks every 90 days or 500 hours. Well, I would advise checking more frequently, something like:
- Check all pressurized components for rust, cracks, or leaks. Immediately discontinue use of the equipment and relieve all system pressure if any of these problems are discovered. (Daily)
- Inspect for air leaks. Squirt soapy water around joints during compressor operation and watch for bubbles. (Weekly)
The Importance of Proper Preventative Maintenance Checks
Carrying out regular preventive maintenance will help your reciprocating compressor and all the inline equipment to run at its optimum performance. If you were to let your reciprocating air compressor shut down, so would your projects.
Regular preventative maintenance will also direct you to any issues before they’re able to propagate into more serious long-term damage. Each compressor manufacturer will provide specific maintenance schedules and maintenance kits they recommend for your model’s proper service; like in the example above.
Following a regular maintenance schedule will not only reduce service calls but will also ensure that you have an efficient reciprocating compressor performance, along with extending the life of your reciprocating compressor. Here’s a guide on Air Compressor Maintenance – How to Guide – Preventative & Ongoing
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
To service a reciprocating air compressor you will need to follow the instructions provided in your owner’s manual. This should provide you will all the steps you need to take and how to complete them. If you cannot locate your owner’s manual, I would recommend contacting the manufacturer directly or searching the internet for it.
Yes, air compressor maintenance is extremely important to help your air compressor avoid premature wear to components and ultimately failure. With a good preventative maintenance checklist, you will be able to keep your air compressor working at its optimum performance and prolong its lifespan.
Every reciprocating air compressor brand is likely to use a different oil from each other. It is therefore recommended that you refer to your owner’s manual for guidance or contact your manufacturer directly. Visit our Air Compressor Oil Types GUIDE – What Oil To Use In Air Compressor for more information!
If you have any questions regarding reciprocating air compressor maintenance, please leave a comment below, with a photo if applicable, so that someone can help you!
